When dealing with information stored in databases, sometimes we encounter the challenge of having the same information repeated in a single column. This is known as duplicate data, and it can cause confusion and errors. In this article, we'll explore a simple yet effective way to find duplicates in single or multiple columns in SQL.
What are Duplicates in SQL?
In SQL, duplicates refer to rows in a table that have identical values in all columns. By using SQL queries, we can identify and deal with repeated values, ensuring our data stays accurate and reliable. The process involves using powerful SQL queries, namely COUNT, GROUP BY, and HAVING, to systematically identify and analyze instances where the same value occurs more than once.
The GROUP BY clause groups the data based on the specific column of interest, while the COUNT function tallies the occurrences of each unique value. The HAVING clause then filters the results, spotlighting only those groups where the count is used for indicating duplicate entries.
Once we spot these duplicates, we can apply some simple methods to remove the duplicates in SQL. These methods not only simplify the process but also ensure that our data remains clean and accurate.
Finding Duplicates in a Single Column
Finding duplicate entries in a single column means looking for the same information to repeat itself. We can use SQL to count how many times something shows up. It also helps organize information based on the specific column we're interested in.
Imagine it's like putting similar things together. Then, we have to pick out the ones that show up more than once. This helps us spot where things are repeated, making it easier to clear up our data.
Syntax:
SELECT column1, column2, ..., -- Apply window function AGGREGATE_FUNCTION(column) OVER (PARTITION BY partition_column ORDER BY order_column) AS result_column FROM your_table;
We will be performing a window aggregate function example for average marks per student.
Table: Employee
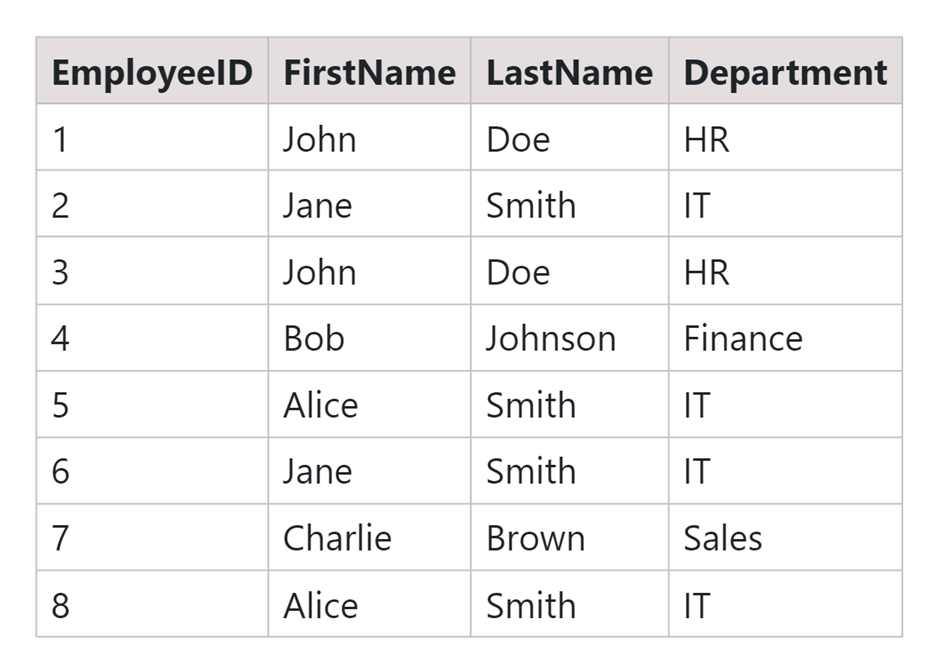
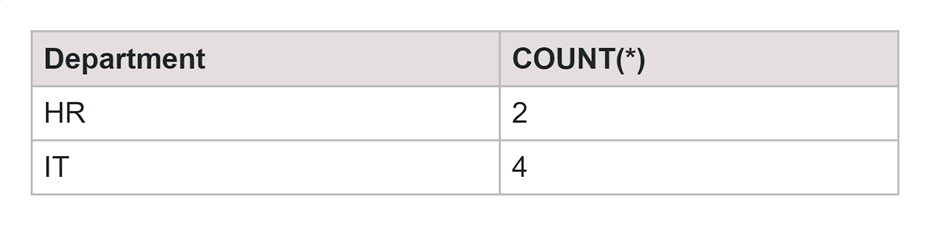
We are finding the duplicates in a single-column Department in this case.
SQL Query:
SELECT column_name, COUNT(*) FROM table_name GROUP BY column_name HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;
Output:
Finding Duplicates in Multiple Columns
When we're trying to find the same stuff in more than one column, we use SQL. It helps us group things based on these columns and then filter out the ones that show up more than once. This way, we can easily spot where combinations of information in different columns repeat, making it simpler to handle and fix these repeating bits of data.
Syntax:
SELECT column1, column2, COUNT(*) FROM table_name GROUP BY column1, column2 HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;
We will use the same table as the above example.
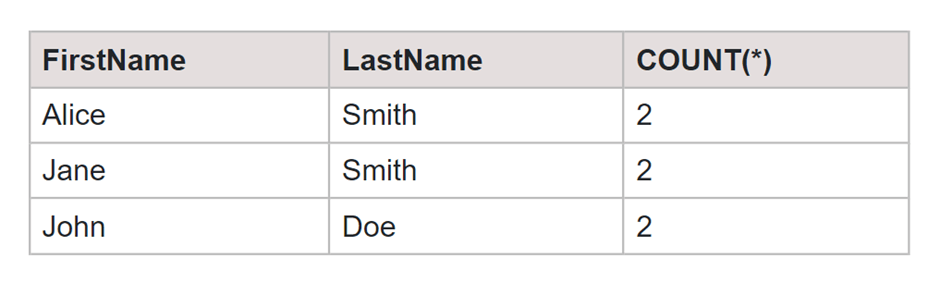
Finding Duplicates in Multiple Columns using the query below:
SQL Query:
SELECT FirstName, LastName, COUNT(*) FROM Employee GROUP BY FirstName, LastName HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;
Output:
Finding Unique Values in a Column Consisting Duplicates
Locating unique values within a column containing duplicates involves using SQL's DISTINCT keyword. This is a handy tool that helps us select and display only distinct or different values from that column. It's a straightforward approach that allows us to focus on what makes each entry unique, even when there are duplicates present. This technique is valuable for maintaining clarity in data analysis and management.
Syntax:
SELECT DISTINCT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name IN ( SELECT column_name FROM table_name GROUP BY column_name HAVING COUNT(*) = 1 );
We will use the same example as above.
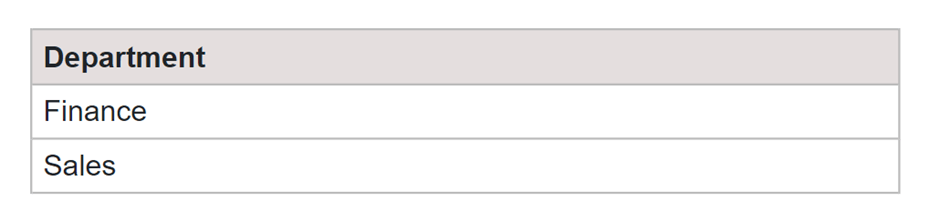
Finding Specific Values in a Column full of duplicate values.
SQL Query:
SELECT DISTINCT Department FROM Employee WHERE Department IN ( SELECT Department FROM Employee GROUP BY Department HAVING COUNT(*) = 1 );
Output:
Conclusion
In a nutshell, finding and fixing duplicate values in SQL is essential for having accurate data. We learned how to find duplicate values in single or multiple columns in SQL. These techniques empower users to streamline their data, resulting in more accurate and reliable database management.