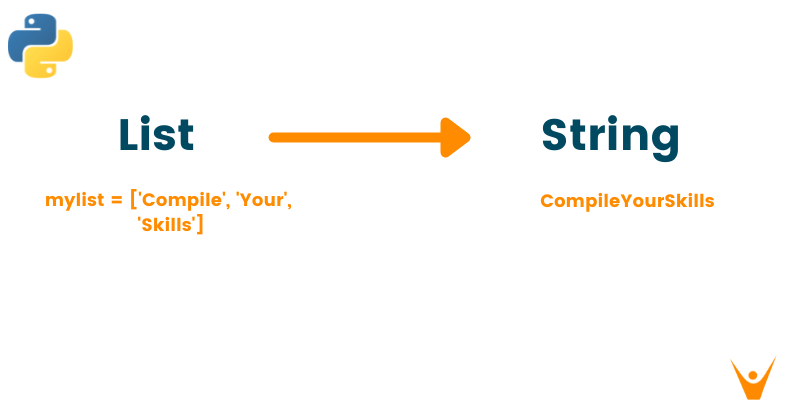
While working with Python data types, there are situations when you want to convert the data collected from one type to another. There are various methods by which we can convert a list to a string in Python with fewer lines of code. But before all that, let us understand what are lists and strings.
What is a List in Python?
A Python list is an ordered and changeable collection of data objects. It is written as commas-separated values inside the square bracket. It can also contain duplicate elements along with negative indexing elements.
The important advantage of the list is that the elements inside the list are not compulsory to be of the same data type. The list undergoes the operations like slicing, concentrating, etc., just like the string operations. Also, you can create a nested list, i.e., a list containing another list.
Example:
sam_list = [10,"favtutor",["compile","it"]] print(sam_list)
Output:
[10, 'favtutor', ['compile', 'it']]
What is a String in Python?
A string is defined as a sequence of characters where a character is a simple symbol. For example, in the English Language, we have 26 characters available. The computer system does not understand characters therefore, it deals with binary numbers. Even though we can see characters on our monitor screens, internally it is stored as a combination of 0s and 1s.
In the Python programming language, a string is a sequence of Unicode characters. It s an immutable sequence data type wrapped inside single or double quotes. That means that once you define a string, you cannot change it.
You can also assign a multi-line string to a variable using triple quotes. Many string manipulation methods are available for string data types like join(), split(), concatenation, etc.
Example:
a = "Compile With Favtutor" print(a)
Output:
Compile With Favtutor
Why Convert the Python List to String?
Python provides a variety of functions and data types to work with. A list, which is an assortment of elements that may consist of any data type, is one of the most practical data types in Python. But occasionally we might need to change a list into a string.
First, if you want to display the contents of a list as a readable string, which is helpful when debugging or when you need to present data in a specific format. Second, sometimes, you may want to store a list in a database. Converting the list to a string allows you to write it to a file or store it in a database column that accepts strings.
There are various methods for turning a Python list into a string. We'll look at three of the most widely used techniques as well: utilizing the enumerate() function, and using the functools.reduce() technique, and using the str.format() technique.
How to Convert List to String in Python?
As mentioned earlier, there are 7 ways to convert a list to a string in Python. Let us study them one by one in detail, along with the example and corresponding output:
1) Iterating through the List
This method will iterate every index of the input list one by one and add it to the empty string. This is the simplest method in Python to convert list to string.
Example:
# converting list to string using iteration def listToString(s): # initialize an empty string string = "" # traverse in the string for element in s: string += element # return string return string # Driver code s = ['Compile ', 'With ', 'Favtutor '] print(listToString(s))
Output:
Compile With Favtutor
2) Using join() method
Every element of the list will be traversed and added to the empty string. The join () method is used to concatenate all these elements and form the final output. This method will fail to work if the list contains integer elements, and therefore the output will be TypeError Exception.
Example:
# converting list to string using join() method # Function to convert def listToString(s): # initialize an empty string string = " " # return string return (string.join(s)) # Driver code s = ['Compile ', 'With ', 'Favtutor'] print(listToString(s))
Output:
Compile With Favtutor
3) Using List Comprehension
As mentioned earlier, the join() method will fail to work if you have integer elements in your input list. But to overcome this failure, you can use the List comprehension along with join() method.
List comprehension will help you to create a list of elements from the existing input list. And later uses a for loop to traverse the elements by element-wise patterns. After the traversal of elements by list comprehension, you can use the join() method to concatenate the traversed elements of the list into an empty string.
Example:
# converting list to string using list comprehension s = ['Compile', 'With', 'Favtutor'] # using list comprehension listToStr = ' '.join([str(element) for element in s]) print(listToStr)
Output:
Compile With Favtutor
4) Using map() function
map() function accepts iterable objects such as tuples, lists, or strings. Hence, it is used to map the elements of the iterable objects with the function provided.
Example:
# converting list to string using map() function s = ['Compile', 'With', 'Favtutor'] # using list comprehension listToStr = ' '.join(map(str, s)) print(listToStr)
Output:
Compile With Favtutor
5) Using Enumerate Function
We may iterate over a list as well as its index at the exact same time using Python's built-in enumerate() function. This function allows us to concatenate strings with a separator to create a single string from a list of strings.
Example:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'date'] separator = ', ' my_string = separator.join(my_list) print(my_string)
Output:
apple, banana, cherry, date
In this example, we first build a string separator called separator as well as a list of strings called my_list. The result is then assigned to a variable called my_string after we connect the strings in the list using the separator using the join() technique. The my_string variable is then printed to the terminal.
A quick and effective approach to do this in Python is by combining the join() technique and the enumerate() function.
6) Using functools.reduce Method
Using the functions.reduce() method is another technique to translate a Python list into a string. With Python's built-in reduce() method, we can apply a function across a list of elements and then receive one value back. This technique can be used to combine a list's items into a string.
Example:
import functools my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'date'] separator = ', ' my_string = functools.reduce(lambda a, b: a + separator + b, my_list) print(my_string)
Output:
apple, banana, cherry, date
In this example, the reduce() method is imported first from the functools module. Then, we define a separator string named separator as well as a list of strings called my_list.
Applying a lambda function that joins two components together with the separator to the list using the reduce() method, we then assign the outcome to a variable called my_string. The my_string variable is then printed to the terminal.
employing functools.reduce() method allows more flexibility and control over the concatenation process, but it is a little more involved than using the enumerate() function.
7) Using str.format() Method
Python's str.format() method is a potent mechanism for formatting strings that enables us to formattily insert values into strings. By adding a list into a string using the syntax, we can utilize this method to change a list into a string.
Example:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry'] my_string = 'The list contains: {}.'.format(my_list) print(my_string)
Output:
The list contains: ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
In the above example, a list called my_list was generated with three members, and it was then inserted into a string called my_string using the str.format() method. The result demonstrates that the list was transformed into a string by using square brackets.
Also, learn how to flatten a list of lists in Python.
Conclusion
List and string have their own importance as data types in Python. This article explains different techniques and methods to convert list data types into strings. It is highly recommended to learn all of them in detail as they are very effective to do the conversion using fewer lines of code.