There may be times when you wish to have a specific type of a variable during programming. Typecasting is a process used to change the variables declared in a specific data type into a different data type to match the operation performed by the code snippet. Python is an object-oriented language that consists of many data types. Today, we will learn List and Tuple data type in python and some methods to convert python list to a tuple in detail.
What is a List in Python?
Python lists are a data structure similar to dynamically sized arrays. The most important feature of python's list is that it need not be homogeneous always. A list can contain elements like integers, strings, and also objects. Therefore, a python list is an ordered and changeable collection of data objects, unlike an array containing a single type of data.
The list is the most versatile and frequently used data structure in python. You can create a list by placing all the elements inside the square brackets([]) separated by commas. All these elements can be further accessed by the index number inside the square brackets, just like arrays. Remember that in the list data structure, indexing begins from zero(0), which means the first element of the list will be accessed with 0 inside the square brackets. Also, the list is mutable. That means you can add, update or remove elements of the list after it has been created. Below example shows the python list in detail:
For Example
list1 = ["favtutor", 1, 2.30] print(list1)
Output
['favtutor', 1, 2.3]
What is Tuple in Python?
Tuples in Python are a data structure used to store multiple elements in a single variable. Just like list data structure, a tuple is homogenous. Therefore, a tuple can consist of elements of multiple data types at the same time. You can create a tuple by placing all elements inside the parentheses(()) separated by commas. Note that the parentheses are an option, however, it is always a good practice to use them while working with tuples in python.
Unlike list data structure, a tuple is immutable. Hence, you cannot add, update or delete the elements of the tuple after creating it. However, if you want to perform any operations on the tuple, a separate copy of the same tuple is created, and then necessary modifications are made. Below example shows a tuple in python programming:
For Example
tuple1 = ("favtutor", 1, 2.3) print(tuple1) # Creating a tuple having one element tuple2 = ("favtutor",) print(type(tuple2))
Output
('favtutor', 1, 2.3) <class 'tuple'>
As shown in the above example, when you declare a tuple with a single element, it will be similar to the string class. Therefore, to avoid this issue, a single comma is placed after declaring a single string to identify the tuple class.
Difference between List and Tuple
|
List |
Tuple |
|
Mutable in nature |
Immutable in nature |
|
Operations are performed better |
Elements can be accessed faster |
|
More memory consumption |
Less memory consumption |
|
Consists of various built-in methods |
Do not consist of any built-in methods |
|
Errors occur frequently |
No such problem occurs |
|
Iterations are time-consuming in list |
Iterations are faster in the tuple |
Convert List to Tuple in Python
As discussed above, the programming requires many operations to be performed on the data. Because the properties and nature of every data structure differ from one another, you have to convert the variable from one data type to another at some point. Similarly, below we have mentioned three common and most widely used methods to convert lists to a tuple in python programming.
1) Using tuple() builtin function
Python language consists of various built-in functions to ease your programming and the tuple() function is one of them. tuple () function can take any iterable as an argument and convert it into a tuple object. As you wish to convert a python list to a tuple, you can pass the entire list as a parameter within the tuple() function, and it will return the tuple data type as an output. Check out the example below for converting “sample_list” into a tuple for better understanding.
For Example
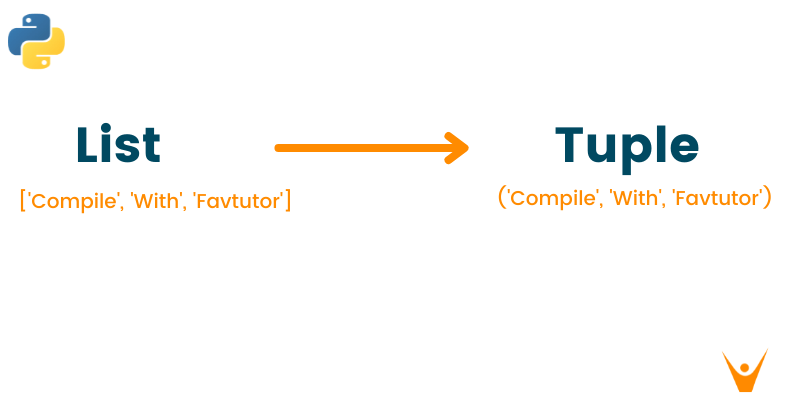
sample_list = ['Compile', 'With', 'Favtutor'] #convert list into tuple tuple1 = tuple(sample_list) print(tuple1) print(type(tuple1))
Output
('Compile', 'With', 'Favtutor') <class 'tuple'>
Here, if you notice, we have used the type() function to identify the variable type that returns tuple object as an output.
2) Using loop inside the tuple
This method is a small variation of the above-given approach. You can use a loop inside the built-in function tuple() to convert a python list into a tuple object. However, it is the least used method for type conversion in comparison to others. Take a look at the below example to understand it in detail:
For Example
sample_list = ['Compile', 'With', 'Favtutor'] tuple1 = tuple(i for i in sample_list) print(tuple1)
Output
('Compile', 'With', 'Favtutor')
3) Unpack list inside the parenthesis
To convert a list to a tuple in python programming, you can unpack the list elements inside the parenthesis. Here, the list essentially unpacks the elements inside the tuple literal, which is created by the presence of a single comma(,). However, this method is faster in comparison to others, but it suffers from readability which is not efficient enough.
For Example
sample_list = ['Compile', 'With', 'Favtutor'] #unpack list items and form tuple tuple1 = (*sample_list,) print(tuple1) print(type(tuple1))
Output
('Compile', 'With', 'Favtutor') <class 'tuple'>
Conclusion
Even though List and Tuple are different data structures in python, it is important to get familiar with their similarities and differences for using them while programming. This article helps you to understand the list and tuple in detail, along with their differences and some common methods to convert python list to tuple. If you wish to study more about type casting in python, check out our article on 6 ways to convert string to float.