Acing the placement season is something that each engineering student aspires for, and the best way to do that is to master Data structures and Algorithms and the core subjects of computer science and engineering. One of the most important data structures to ace the placements is Trees, and in this part of the tutorial, we are going to discuss the level order traversal of a binary tree and its python code. Hence, to get a clear understanding of level order traversals let us first get acquainted with binary trees.
What is Binary Tree?
A binary tree is a tree-type non-linear data structure, where each parent has a maximum of two children. Each level in a binary tree is the number of nodes between that node and the root node, and each node consists of a left and right reference and stored data element. The top node for the binary tree is called the root node. Parent nodes hold other sub-nodes and leaf nodes do not have any children. The basic terminologies involved in binary trees are as follows:
- Node: Each node contains a left and right child.
- Leaf Node: The node of the tree which doesn’t have any child nodes.
- Root: Topmost node of the tree.
- Parent: Each node (other than the root node) in a tree that has at lea
- Internal Node: Nodes with at least one child.
- Depth of a Tree: The number of edges from the tree’s node to the root node.
- Height of a Tree: Number of edges from the node to the deepest leaf node, it is also called the root height.
Basic Traversal Techniques of Binary Tree
There are three common ways of binary tree traversal:
1. Inorder Traversal :
i) Consider the nodes in the left subtree,
ii) Then go to the root node
iii) Then consider all the nodes in the right subtree
2. Preorder Traversal :
i) First, all the visit root node
ii) Consider all the nodes in the left subtree
iii) Consider all the nodes in the right subtree
3. Postorder Traversal :
i) Go to all the nodes in the left subtree
ii) Consider all the nodes in the right subtree
iii) Go to the root node
We can also use level order traversal, where we visit every node on a level before going to the lower level. Node values at each level should be stored in a 2D array of elements. Given a pointer to the root node of the binary tree, we can find the level order traversal of this tree by adding the elements at each level to an array and returning the final array. In this type of breadth-first traversal, nodes are traversed level by level from left to right.
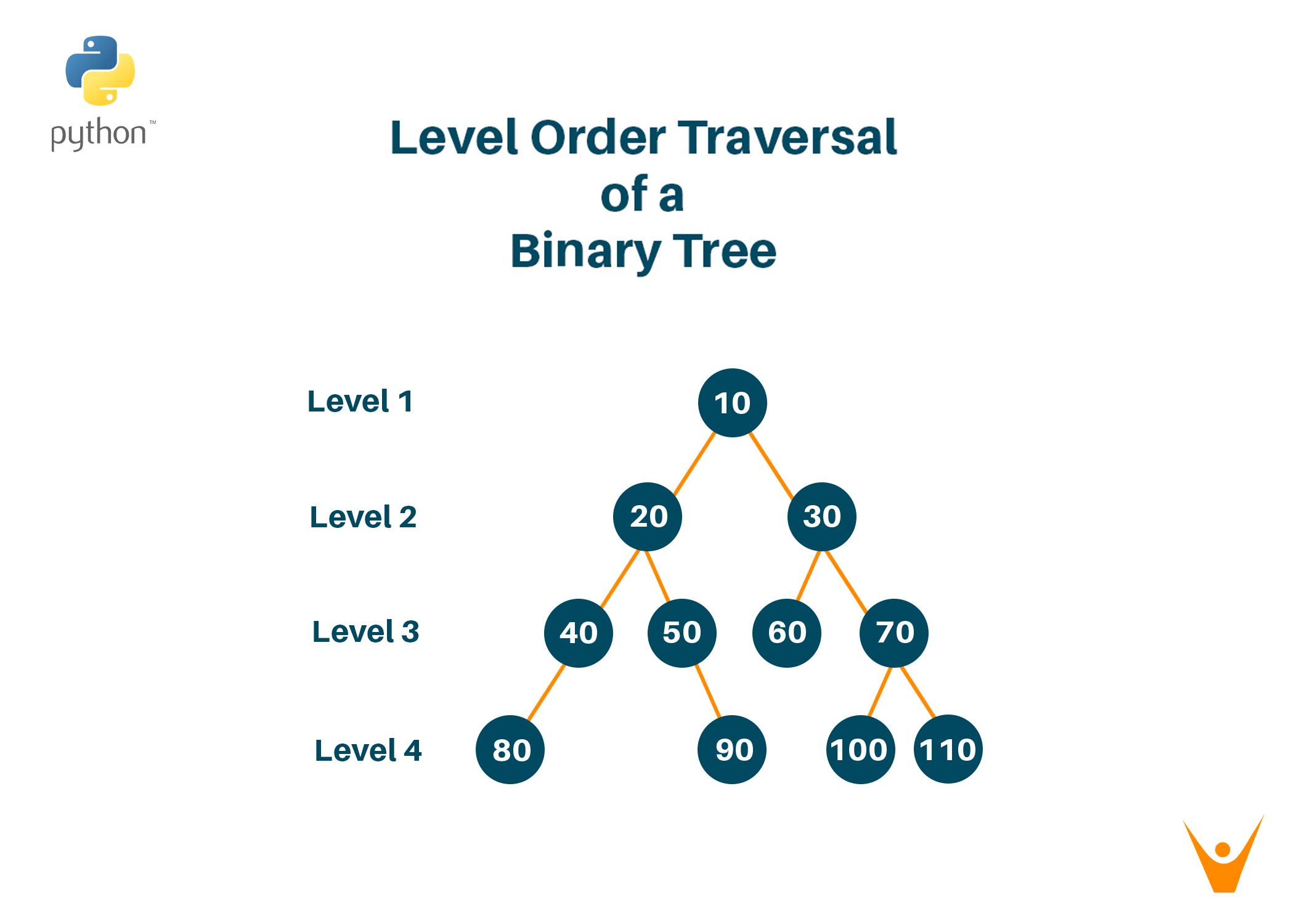
Example of Level order Traversal
The figure below shows a binary tree with 4 levels indicated.
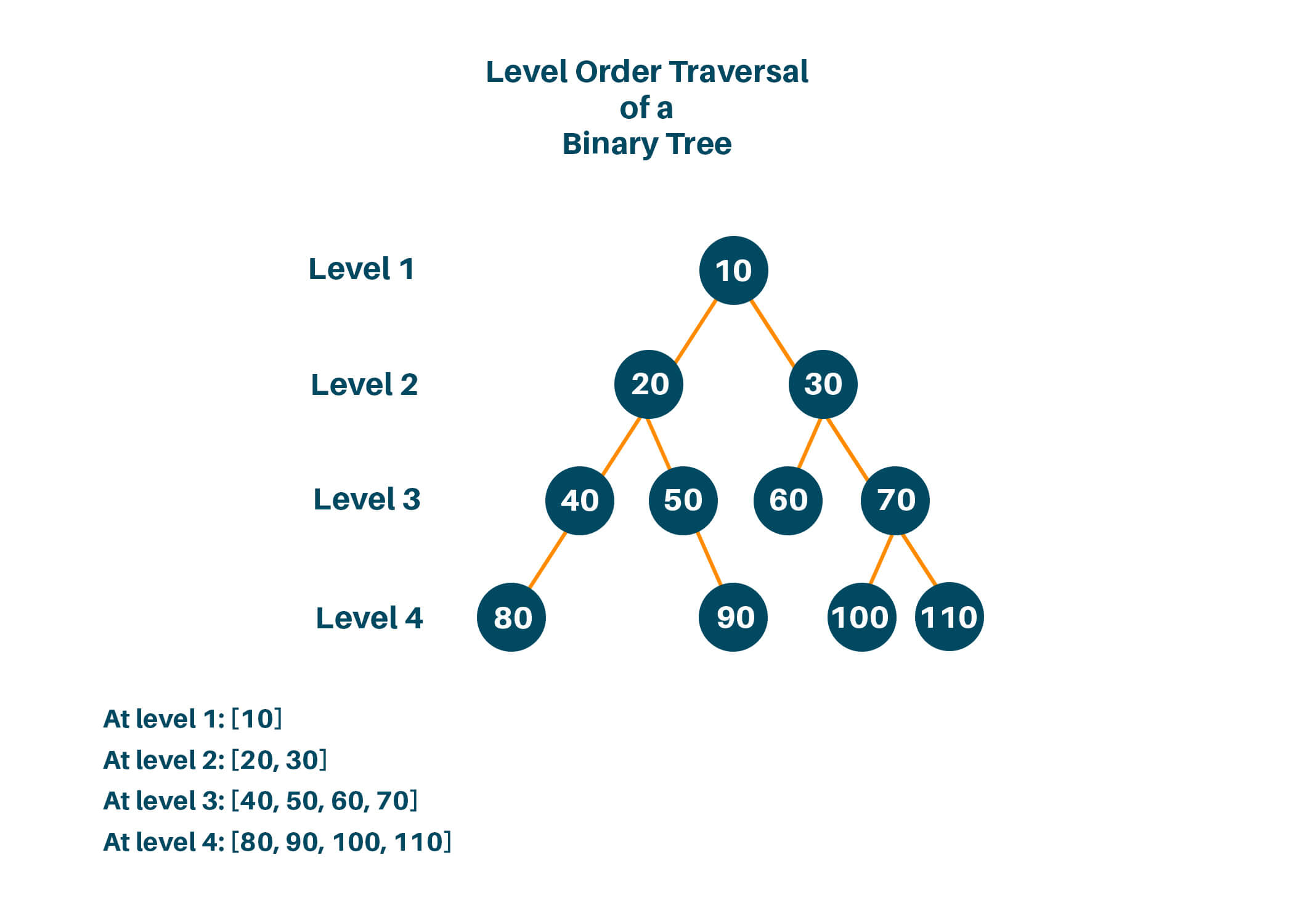
The level order traversal for the tree will be:
Level 1: [10]
Level 2: [20, 30]
Level 3: [40, 50, 60, 70]
Level 4: [80, 90, 100, 110]
Algorithm For Solving Level Order Traversal
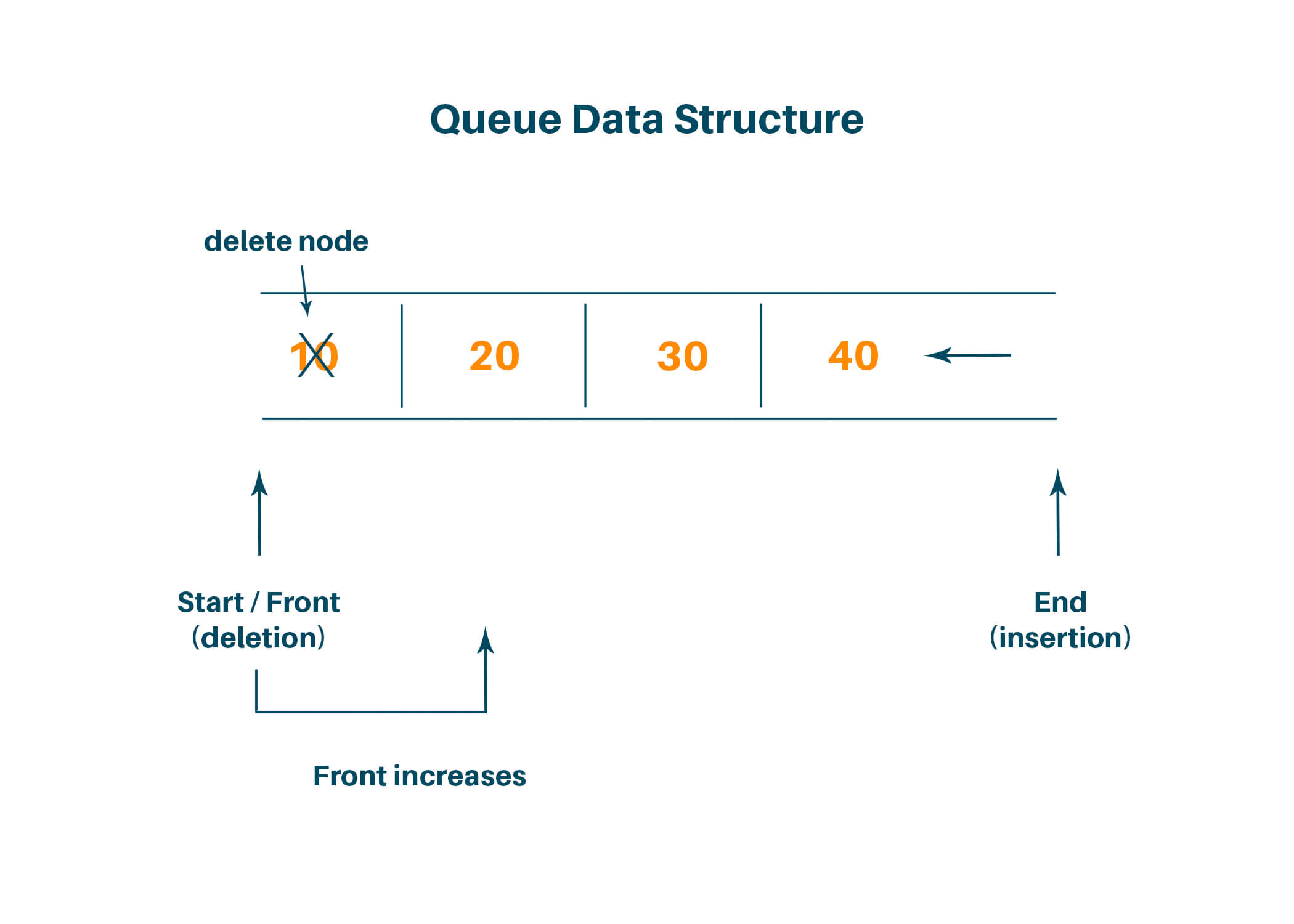
Queue Data Structure
To solve this problem, we use a queue data structure that follows the First In First Out technique (FIFO). The rear end is always used to insert the data ie to enqueue and the other end is used to remove data ie dequeue. Given below image below explains the basic working of a queue data structure.
Implementation (Step-by-Step):
Let us first understand the algorithm with the help of an example, consider we have a binary tree with 11 as the root node and the binary tree looks something like this:
.jpg)
Step 1: To get a better intuition of the algorithm, visualize the binary tree and mark the levels as mentioned in the image given above.
Step 2: Create a queue data structure and enqueue the elements from each level, hence we add 11 to the queue and initialize an empty array to store the result after completing the level order traversal, ie.
answer = []
 (1).jpg)
Step 3: Use a while loop to iterate through the elements of the queue until and unless there are no elements present, find the number of elements in the queue and initialize a variable to store the number of elements in queue currently, ie.
cs = 1
Step 4: Dequeue the elements until the queue is empty and decrement cs and store the dequeued element into a current list/array, ie.
Now:
cs = 0
currList = [11]
Step 5: Check for the left and right child of the current binary tree node and then enqueue it to the original queue.
Step 6: If cs = 0, add the currList to the answer array, ie.
Now:
answer = [[11]]
Repeat steps 3 and 4, hence we dequeue 13 after checking the left and right child of 13 we enqueue 19 and 26.
Now:
cs = 2
currList = [13,
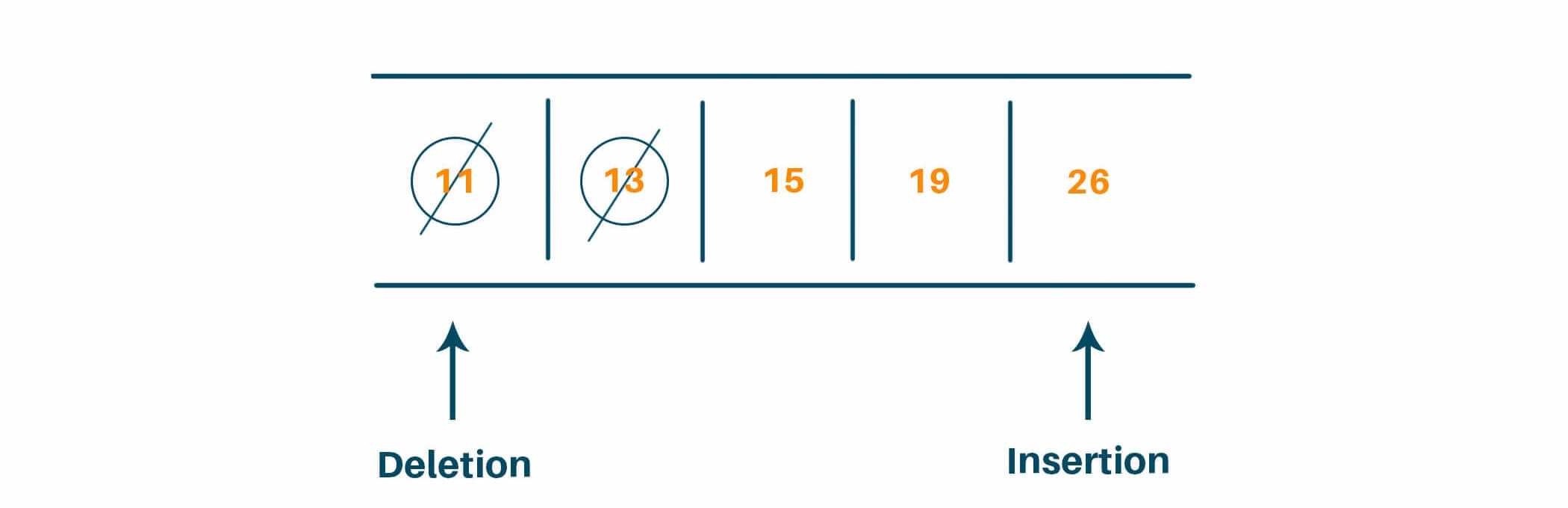
Now:
cs = 1
currList = [13, 15
.jpg)
We again repeat steps 3 and 4, hence dequeue 15 and enqueue 17 (left child of 15) and 23 (right child of 15)
Now:
cs = 0
currList = [13, 15]
Hence we add this currList to answer
answer = [[11], [13, 15]]
We repeat this process, iteratively in a while loop and finally, we get
answer = [[11], [13, 15], [19, 26, 17, 23], [21, 22, 25]]
Level Order Traversal Python Code:
# To import queue datastructure import collections # Code to implement a binary tree class TreeNode: def __init__(self, val): self.val = val self.left = None self.right = None # Function for level Order Traversal def levelOrderTraversal(root): ans = [] # Return Null if the tree is empty if root is None: return ans # Initialize queue queue = collections.deque() queue.append(root) # Iterate over the queue until it's empty while queue: # Check the length of queue currSize = len(queue) currList = [] while currSize > 0: # Dequeue element currNode = queue.popleft() currList.append(currNode.val) currSize -= 1 # Check for left child if currNode.left is not None: queue.append(currNode.left) # Check for right child if currNode.right is not None: queue.append(currNode.right) # Append the currList to answer after each iteration ans.append(currList) # Return answer list return ans root = TreeNode(1) root.left = TreeNode(2) root.right = TreeNode(3) root.left.left = TreeNode(4) root.left.right = TreeNode(5) # Check if the algorithm work print(levelOrderTraversal(root))
Output:
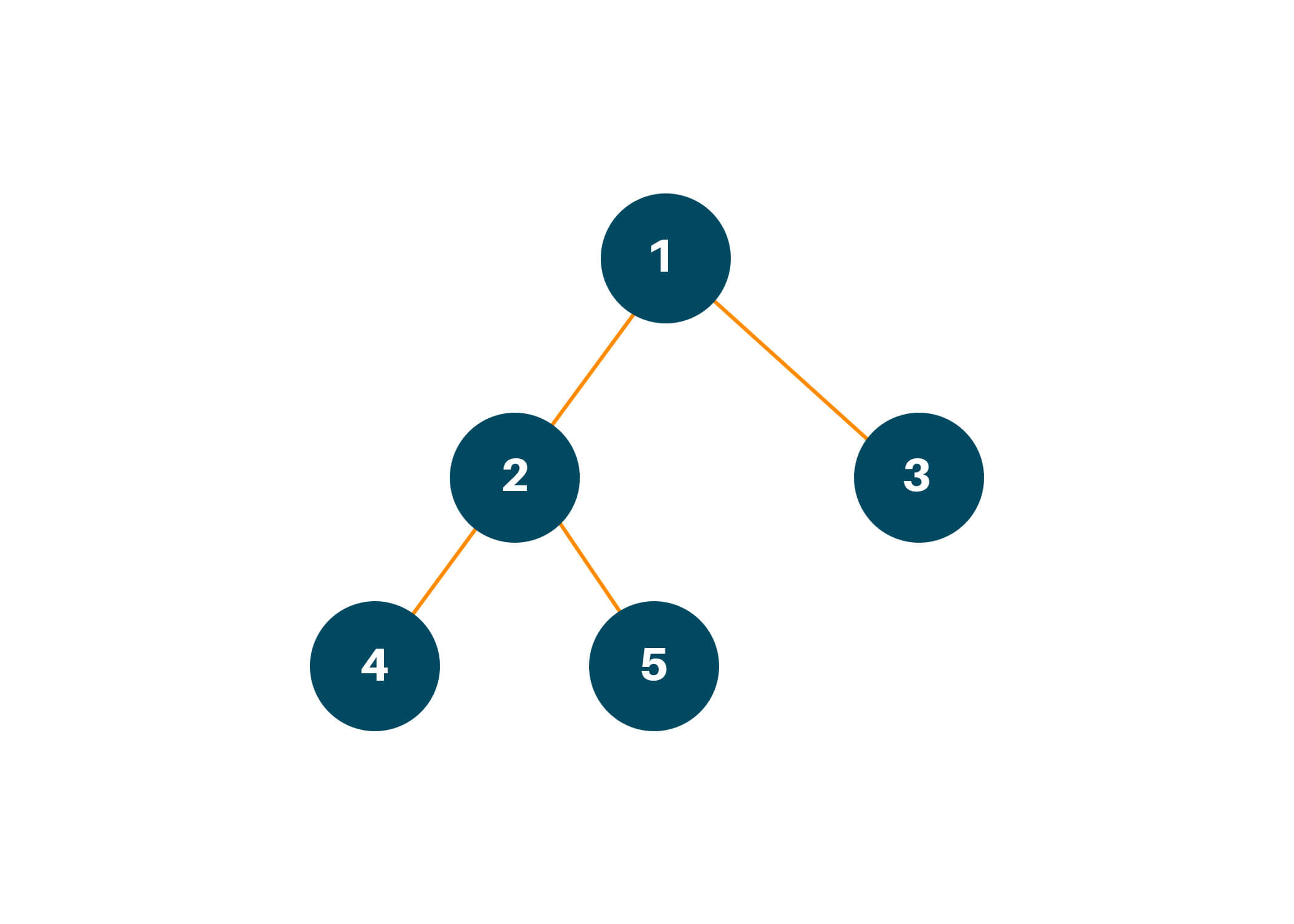
[[1], [2, 3], [4, 5]]
Time and Space Complexity:
The time complexity of the algorithm is O(n) as we iterate through elements of the binary tree for level order traversal only once.
And the space complexity is also O(n) as we used extra space for creating dequeue from the collections library in python.
Where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
Applications:
It is used to display the data in the same order as stored in the array representation of a complete binary tree.
Conclusion:
In this tutorial, we learned how to find the level order traversal of a binary tree and its python code, a basic introduction of binary trees. We also learned the meaning of level order traversal and got a better intuition of queue data structures.