The GROUP BY is a handy tool for managing databases. Ordinarily, grouping is done by a single attribute, like organizing cars by model. But, this article will show you the way to use GROUP BY in SQL for multiple columns, much like sorting cars by model and type. We'll study the fundamental features such as the use of conditions and filters, to optimize your data analysis.
What is GROUP BY in SQL?
The GROUP BY clause in SQL is used to group rows that have the same values into summary rows. It simplifies data organization by cataloging it according to shared characteristics.
It's often used in conjunction with aggregate functions like SUM(), COUNT(), AVG(), MAX(), or MIN() to perform operations on these groups of rows. Learn more about Window Functions in SQL here.
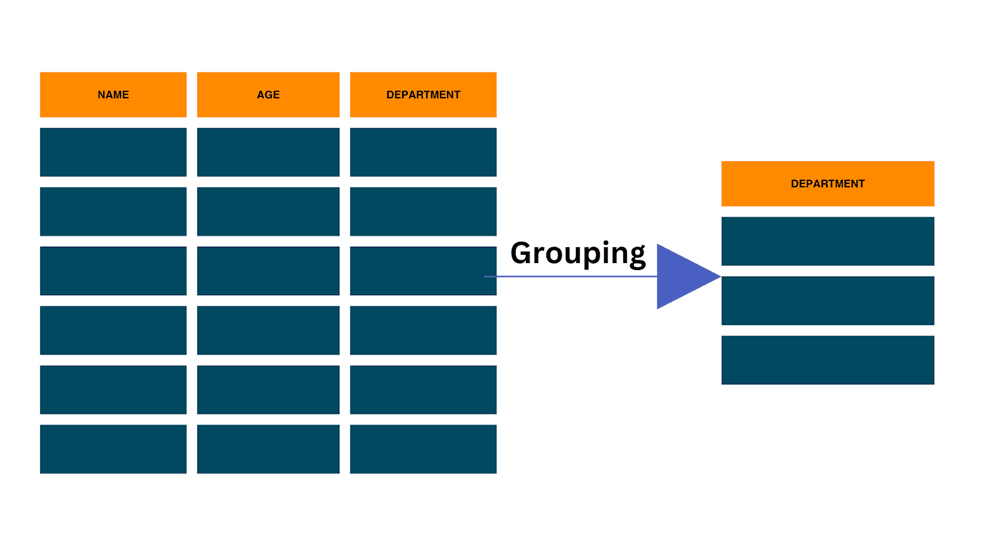
We begin GROUP BY by picking one or more columns in the SELECT statement. It forms unique groups, each with matching values in the chosen columns. Using together grouping and aggregation allows us to calculate stats inside each group.
Group By is also used to find duplicate values in SQL.
GROUP BY with Multiple Columns
GROUP BY with Multiple Columns can be compared to sorting out your clothes based on two criteria. Doing this not only makes the data easier to understand but also helps in finding patterns. It ultimately improves our knowledge of the data. Here's an overview of GROUP BY at its use in SQL and how it adds efficiency to your data.
Syntax:
SELECT column1, column2, aggregate_function(column3)FROM table_nameGROUP BY column1, column2;
Let us understand this through an example:
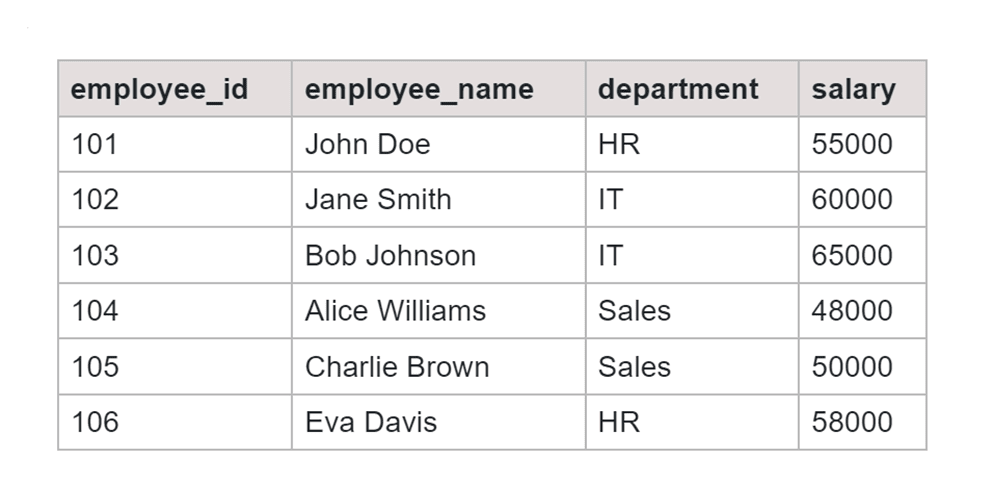
Table: Employee
SQL Query:
SELECT department, AVG(salary) AS avg_salary FROM employee GROUP BY department;
Output:
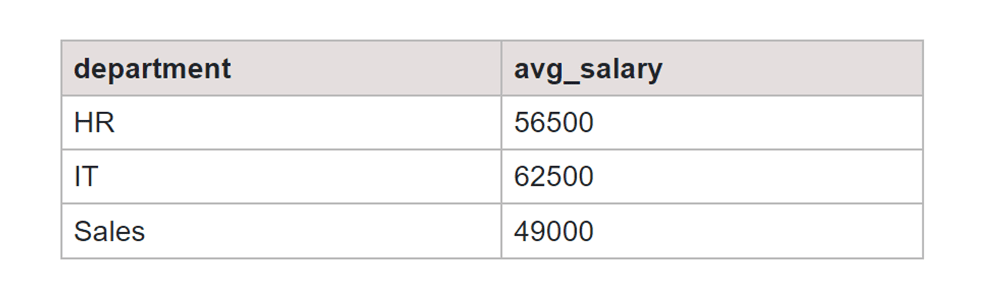
In simple terms, SQL GROUP BY with multiple columns does more than just sorting; it includes adding a hierarchy of information, counting, and categorizing how you look at your data. It's more than arranging though, this feature brings more structure to your data collection. This function improves order and insights to your dataset.
GROUP BY with CASE in Multiple Columns
Utilizing CASE and Multiple Columns in SQL really helps to clean up our data. Rather than just grouping statements, moreover, it allows us to give different views of the same data, it enables us to make specific data using CASE statements.
Just imagine creating different groups to simplify the study of your data, it's exactly like that! Now, let’s dive into how this combination of CASE in multiple columns enhances our understanding of data.
Syntax:
SELECT column_name,CASEWHEN SUM(column_name) > some_value THEN 'Condition’ELSE 'Condition 2'END AS new_column_nameFROM table_nameGROUP BY column_name;
We will use the same 'Employees' table example.
Grouping by department and a custom category based on salary.
SQL Query:
SELECT department, CASE WHEN AVG(salary) > 60000 THEN 'High Salary' WHEN AVG(salary) > 50000 THEN 'Medium Salary' ELSE 'Low Salary' END AS salary_category FROM employee GROUP BY department;
Output:
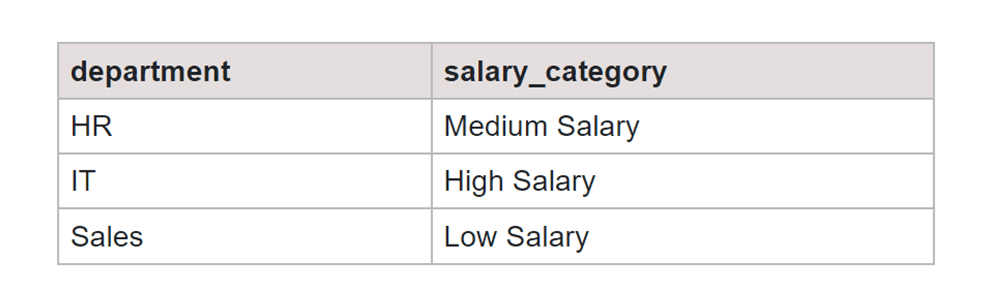
GROUP BY with HAVING COUNT Clause
Think of GROUP BY with a HAVING and COUNT Clause in SQL as a special kind of filter. It helps you make summaries by letting you choose which groups to show based on certain conditions and criteria. Imagine, you want to sort items and only want to keep groups that meet your specific needs. Using GROUP BY with HAVING and COUNT lets you analyze data with specific conditions or criteria.
Syntax:
SELECT column1, COUNT(column2) AS column_nameFROM table_nameGROUP BY column1HAVING COUNT(column2) > threshold;
We will use the same 'Employees' table example.
Grouping by department and selecting only those with more than one employee.
SQL Query:
SELECT department, COUNT(employee_id) AS employee_count FROM employee GROUP BY department HAVING COUNT(employee_id) > 1;
Output:
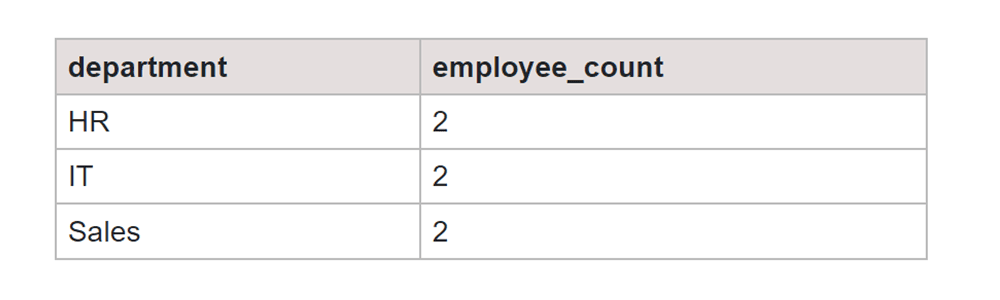
Uses of GROUP BY Function
Following are the uses of the GROUP BY Function:
- Organizing Data: GROUP BY organizes your data, similar to sorting your clothes into wardrobes. It arranges information based on given conditions.
- Trends and Patterns: Having a list of students and marks helps you see the GROUP BY pattern, which shows when a student's performance is getting better or worse.
- Aggregated Columns: Together with GROUP BY CASE, each column is analyzed. It’s like creating your identification for things. For example, you can categorize the type of cars into categories such as ‘SUV’, ‘Hatchback’, or ‘Sedan’.
- Filtering Data: It allows you to focus only on the information you need and select groups that meet specific conditions.
- Finding Data: GROUP BY is like a shortcut for finding information faster. Instead of going through every detail, it lets you focus on the larger picture, making your searches efficient and smoother.
Conclusion
To sum it up, using SQL GROUP BY with multiple columns is a useful method for organizing and analyzing data. It's like sorting your things into more than one category. If you have some questions about it in your homework, you can get SQL Assignment help from us.